Dithering over the economy and T’s electable abilities as well as the HHS, CDC, FDA’s failures, this group deferred to T.
What a mess…what a tragedy.
Dr. Robert Redfield, the director of the Centers for Disease Control, flanked Donald Trump at the podium in the White House briefing room. It was February 29th, the day of the first reported U.S. death from the coronavirus, and the president fielded an urgent question: “How should Americans prepare for this virus?” a reporter asked. “Should they go on with their daily lives? Change their routine? What should they do?”
In that moment, America was flying blind into a pandemic; the virus was on the loose, and nobody quite knew where. The lives of tens of thousands hinged on the advice about to be delivered by the president and his top public-health advisers. Trump began: “Well, I hope they don’t change their routine,” before he trailed off, and, quite uncharacteristically, called on an expert to finish the response. “Bob?” he said. “Do you want to answer that?”
…Even as he spoke, Redfield knew the country should be taking a different course. The Coronavirus Task Force had resolved to present the president with a plan for mitigation efforts, like school and business closures, on February 24th, but reportedly reversed course after Trump exploded about the economic fallout.
…
Patty Murray is the ranking member of the Senate’s top health committee, and represents Washington state, the nation’s first coronavirus hot spot. She blames the administration for a delay that “overwhelmed the health care system and resulted in tens of thousands of deaths.” And she singles out Redfield, in particular, for “dereliction of duty.”
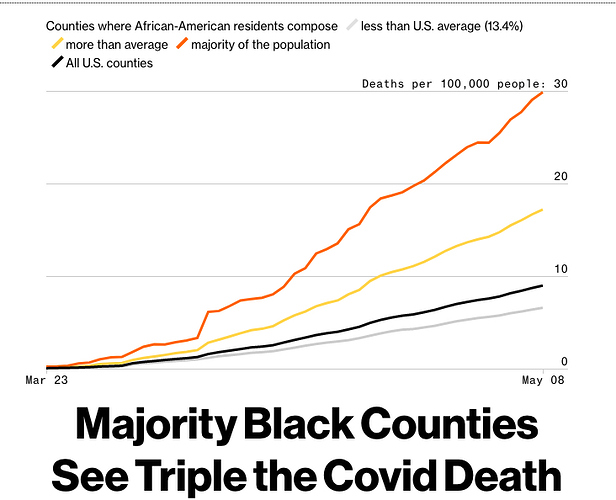
Despite months of alarms that the coronavirus was lurking at our doorstep, the Trump administration failed to mount an urgent response until the nation was engulfed and overwhelmed by the pandemic.
“We had ample notice to get our country ready,” says Ron Klain, who served as President Obama’s Ebola czar, and lists the rolling out of testing, securing protective equipment, and building up hospital capacity as necessary preventative steps. “We spent all of January and February doing none of those things, and as a result, when this disease really exploded in March, we weren’t prepared.”
The government leaders who failed to safeguard the nation are CDC Director Redfield; FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn; Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar; and of course, President Trump. Together, these men had the power to change the direction of this pandemic, to lessen its impact on the economy, and constrain the death toll from COVID-19. Each failed, in a series of errors and mismanagement that grew into a singular catastrophe — or as Jared Kushner described it on Fox & Friends, “a great success story.”
A tall man, with a tan, freckled head, and a snow-white chinstrap beard, Redfield stepped to the podium. “The risk at this time is low,” Redfield told the country. “The American public needs to go on with their normal lives.”
…
THE ZEALOT
The front-line agency built to respond to a pandemic, the CDC, was placed in unreliable hands. Dr. Robert Redfield is a right-wing darling with a checkered scientific past.
Redfield, a devout Catholic who was then a prominent HIV researcher in the Army, wrote the introduction, calling for the rejection of “false prophets who preach the quick-fix strategies of condoms and free needles.”
…
THE INSIDER
The CDC reports to the Department of Health and Human Services, led by Alex Azar, a former executive for the pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly who gained infamy, in his five-year tenure, by doubling the price of insulin.
Azar is a creature of the GOP establishment: He cut his teeth as a Supreme Court clerk to Antonin Scalia, worked with Brett Kavanaugh on the Clinton-Whitewater investigation under special counsel Ken Starr, and served as a deputy HHS administrator in the George W. Bush era, before becoming Eli Lilly’s top lobbyist. Azar, 52, is the type of corporate leader Republicans have long touted as capable of driving efficiencies in the unwieldy federal bureaucracy.
…
Rick Bright directed HHS’s Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority until his ouster in April. In a whistleblower complaint, he reveals he warned Azar on January 23rd that the virus could already be spreading in the U.S. but “we just don’t have the tests to know one way or the other.” Bright accuses HHS leadership of “a lax and dismissive attitude” toward the coronavirus, and singles out Azar for “downplaying this catastrophic threat.”
…
UNREADY AT THE FDA
Stephen Hahn had been on the job at the FDA for barely a month. A bald, 60-year-old of modest height, Hahn has an impeccable résumé — he served as chief medical executive at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center — but he had no experience running a government agency.
…
THE BLACK-SWAN EVENT
With the private sector offline, the stakes for the CDC test could not have been higher. The CDC had a peerless reputation. Despite its underfunding, it was considered a crown jewel of public-health agencies.
“Starting with the CDC test makes perfectly good sense,” says Kathleen Sebelius, who served as HHS secretary in the Obama administration. The CDC performed ably during the H1N1 outbreak on her watch. “Within two weeks of knowing what H1N1 looked like,” she recalls, “the CDC had millions of test kits to push out to the states and around the world.” There was little reason to think that the CDC could not perform the same in this crisis.
The CDC — itself subject to FDA regulation — obtained emergency approval of its own test on February 4th and began shipping out kits, manufactured in its own laboratories, to roughly 100 public-health labs across the country. The CDC test was complex, including two steps that tested for genetic markers of the novel coronavirus, and a third meant to rule out other known coronaviruses. But when state labs began testing, the unthinkable happened: The third prong failed, providing inconclusive results.
…
The crisis was acute: The U.S. had a single test for the coronavirus, and it could only be run at the CDC’s Atlanta headquarters, as well as a handful of state labs that had been able to make assay work. This bottleneck would require extreme rationing of tests, to patients who’d traveled to foreign hot spots and tested negative for other diseases. The criteria were so strict that the CDC allegedly refused a test to a nurse who fell ill after treating COVID patients.
One might excuse Alex Azar for his failure to manage up. At the time the CDC tests began to fail, Trump was in the throes of denial, praising President Xi of China on Twitter — “He is strong, sharp and powerfully focused on leading the counterattack on the Coronavirus” — and predicting the disease “goes away in April with the heat.”
But Azar proved equally hapless at managing down. Instead of engineering a workaround to the unreliable CDC test, or leaning on his private-sector connections to jump-start commercial testing, Azar insisted that the original kit be fixed. He reportedly rejected use of the WHO test, out of concern that the test was unreliable. (CDC and HHS officials also underscored that the WHO test, itself, would have had to go through the sticky wicket of FDA regulation.)
The impulse at Redfield’s CDC was to slow down, Becker says, to guard against producing a second, flawed batch of test kits. Hahn’s FDA, meanwhile, was focused on its role as the CDC’s regulator, intent on rooting out the flaw in the original test it had approved. The agencies were soon enmeshed in a bureaucratic struggle so toxic that an FDA diagnostic expert sent in to troubleshoot was briefly locked out of CDC facilities. (HHS blames a scheduling conflict.)
In interviews with Rolling Stone, FDA officials accused the CDC of providing incomplete and misleading information, of downplaying the number of public labs that were unable to run the test, and of signaling to the FDA that the CDC would be able to fix the problem on its own. A CDC representative, in turn, claimed that the FDA slowed the CDC’s response by throwing up redundant regulatory hurdles. The FDA would ultimately conclude that the “CDC did not manufacture its test consistent with its own protocol” and that a “manufacturing issue” — believed to be contamination at the CDC’s lab — rather than a design defect, was responsible for the flawed results.
Sebelius says it is par for the course for bureaucracies to seize up in a crisis: “The default position is do nothing, to stand behind the regs, and say, ‘We can’t move.’ ” But she insists that the foot-dragging and finger-pointing had a solution: leadership at the parent agency, HHS, by Azar. “I can guarantee you that the secretary can get their attention,” she says.
…
Behind closed doors , top administration officials were starting to grapple with the seriousness of what the United States was facing — and to understand, at least intuitively, what the CDC’s failed testing regime was hiding: Containment of the coronavirus was failing, and economy-crippling mitigation would soon be necessary.
By Valentine’s Day, the National Security Council had reportedly developed a memo offering social-distancing guidelines, including school closures, “wide-spread ‘stay at home’ directives” and “cancellation of almost all sporting events, performances, and public and private meetings.” The role of asymptomatic carriers in spreading the coronavirus was becoming clearer, leading a top HHS official to warn of “a huge hole on our screening and quarantine effort.” By February 24th, the Coronavirus Task Force, Redfield included, had reportedly resolved to recommend a plan to Trump called “Four Steps to Mitigation.” But before Trump could be briefed, Messonnier had the grave misfortune of telling the truth. In a February 25th briefing with reporters, she warned of a wide coronavirus outbreak in the United States: “It’s not so much a question of if this will happen anymore, but rather more a question of exactly when.” She cautioned that under social-distancing measures, many Americans could lose income and that “disruption to everyday life may be severe.”
“Dr. Messonnier’s statements were right on,” says Frieden, the former CDC head, who says he relied on her as one of the nation’s top public-health specialists in respiratory viruses. But after Messonnier’s comments contributed to massive stock-market losses, Trump thew a fit. He exploded at Azar and reportedly threatened to fire the CDC scientist.
Trump soon announced a major change of course. Pence would be taking over the task force, sidelining Azar. Trump himself minimized the threat of the disease, calling coronavirus “a flu,” and insisted that infections had peaked: “We have a total of 15 people” diagnosed with COVID-19, he said. “The 15, within a couple of days, is going to be down to close to zero.”
…
The testing breakdown had left the nation blind to the true scope of the outbreak. By March 1st, the CDC’s official tally of coronavirus cases had spiked from the 15 cases touted by Trump to 75. But researchers at Northeastern University have now developed models showing there were likely 28,000 infections at the time, in just five major cities, including New York and Seattle. The Seattle Flu Study — bucking red tape from the FDA and CDC — had begun a rogue effort to test swab samples it had collected using its own lab-developed test. By early March, the testing had uncovered a bevy of undiagnosed coronavirus infections. Dr. Helen Chu, the project’s lead scientist, told The New York Times that she realized then, with horror, “It’s just everywhere already.”
At this moment, shutting down the economy was inevitable — it was just a question of when the measures would be implemented. But scientists believe up to 90 percent of the human toll was still avoidable, had the government moved immediately to implement social-distancing measures. Instead, the administration persisted in its “Do nothing” message parade.
…
A PRESIDENT ADRIFT
Having plunged the nation headlong and unprepared into the deadliest disease outbreak in a century, President Trump is now proving to be one of the greatest obstacles to an effective national response.
Sebelius ultimately blames Trump for failing to end the infighting and fix the testing failure. “The White House has a unique way to get agencies’ attention, by making it clear that they want a solution, and everybody at the table with that solution within 24 hours,” she says. “If the president wants this to happen, it will happen.” But on his visit to the CDC in Atlanta, Trump had made an extraordinary admission: That he did not want to let passengers from a cruise ship, then suffering an outbreak off the California coast, to come on shore because the tally of patients would rise. “I like the numbers being where they are,” Trump said
…
Trump has extraordinary powers to set the country on a better course — but he hasn’t used them. “What has been really terrifying to watch is that the federal government has refused to use the unique purchasing authority, the unique production authority, that no state can mobilize,” Sebelius says. What’s more, rather than supporting governors, Trump has been undermining them, “creating a system of chaos and competition, as opposed to collaboration, that has made the situation worse for most states.”
…
In the event that Trump is still president when a vaccine becomes available, Sebelius argues that the loose confederations that have formed in the Northeast, Midwest, and Pacific states to coordinate their reopenings may need to band together in a shadow government to sidestep Trump. “Maybe governors will put together their own system,” she says, “and ignore what’s happening in the White House.”situation worse for most states.”.